
- About Us
- Investor Relations
- ESG
- Product & Service
- Customer Service
Customer Service
- Visiting Taiwan

Taiwan Mobile Co. (TWM) established a risk management policy in 2011, and relevant policies and procedures were disclosed on the official website. The policy was revised for the third time by the board of directors in 2022 as the highest principle for risk management. The Company actively plans risk management policies, the organizational structure and risk management systems; potential risks in the operation of the Company are dealt with on a preventive basis before they occur.
The Risk Management Committee (RMC) was set up in 2015 after the approval of the board of directors to reinforce the organization’s risk management mechanism. Our Chief Finance Officer is assigned to be the chairman of RMC by chairman of board. All the records of RMC operations are submitted to the chairman of the board for approval. Starting from 2021, the status will be reported to the board of directors at least once a year to ensure that all risks are effectively managed.
The Internal Audit Office conducts an annual review of the risk management mechanism and annual year-end risk assessments, and rates the importance and possibility of each risk, then calculates the risk value according to the results of the rating. The risk value becomes the basis for the following year's audit plan.
In 2024, the audit results did not show any internal control deficiencies and abnormalities. Nevertheless, 82 concrete suggestions for improving operational procedures were proposed as ways to improve the quality of management. The improvements and suggestions are to be tracked on a quarterly basis until they have been completed.
TWM integrates and manages various important risks that may affect operations and profits by proactive and cost-effective manner along with a response mechanism from the three-level risk management.
The company's important risks include "Operating risk", "Risks related to information privacy and security", "Innovation risk"... and so on. Please read the detail content in the company's annual report.
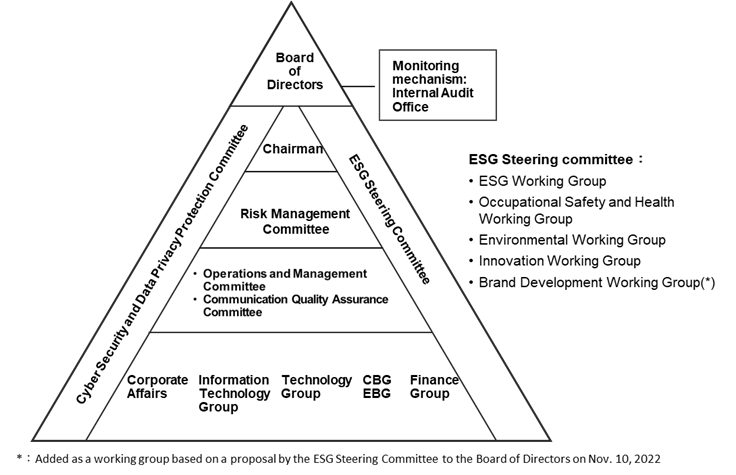
| Responsible unit (Risk Ownership) | Function | |
| Operational Risk Ownership (first line) | Corporate Affairs, Information Technology Group, Technology Group, Consumer Business Group, Enterprise Business Group, Home Business Group, Finance Group | Risk factors are analyzed and assigned to responsible units to monitor and ensure timely and effective detection. Each unit shall ensure, on a daily basis, that risks are kept under acceptable levels. Should there be any changes in condition or other factors, the responsible unit shall report these to the Company for an appropriate course of action. |
| Risk Management and Compliance Oversight (second line) | Risk Management Committee* | Integrate the Company's risk management framework and internal control mechanism. Execute risk management strategies and conduct a review of the efficiency of the overall risk management mechanism. Exercise control over the four following committees: |
| 1) Operations and Management Committee | Conduct periodic reviews of each business group’s operating targets and performance to meet the Company’s guidance and budget. | |
| 2) Communication Quality Assurance Committee | Ensure and manage network communication quality. | |
| ESG Steering Committee | Establish a functional committee governance system, strengthen management functions, and commit to the implementation of corporate social responsibility and sustainable management. | |
| 1) ESG Working Group | Integrate operations and core resources to promote the Company’s ESG policies to move toward sustainable development. | |
| 2) Occupational Safety and Health Working Group | Supervise and minimize potential risks to workers’ health and safety. | |
| 3) Environmental Working Group | Develop and manage the Company's policies and objectives for environmental and energy management. | |
| 4) Innovation Working Group | Integrate the Company’s innovation strategies and establish a management mechanism. | |
| 5) Brand Development Working Group | Implement the brand spirit of "Open Possible" and build a seamless brand experience from the inside out through employee conduct, products and services, internal and external working environments, and marketing communications. | |
| Cyber Security and Data Privacy Protection Committee | Demonstrate the Company’s commitment to these principles by investigating reported breaches of information privacy principles and policies, and, if necessary, take appropriate corrective measures. | |
| TOP | Board of Directors | Responsible for assessing material risks, designating actions to control these risks and keeping track of their execution. |
| Independent Audit Unit (third line) | Internal Audit Office | Regularly monitor and assess potential and varying levels of risks that the Company might face and use this information as a reference for drafting an annual audit plan. Report any discrepancy to the concerned unit chief and ensure that remediation efforts are completed. |
- *Note
TWM sets up RMC which is chaired by the Chief Financial Officer and consists of 6 members including the chairman of board and the highest-ranking officer or their agent from each major risk management area. RMC is responsible for supervising and strictly controlling risk management related issues, and promotes a risk management-oriented management model to achieve the goal of improvement continuously.
The RMC is hold at least once every six months, and communicates with various functional committees as “Operations and Management Committee”, “Occupational Safety and Health Working Group”, “Communication Quality Assurance Committee”, “Environmental Working Group”, “Cyber Security and Data Privacy Protection Committee” , “ESG Working Group” and “Innovation Management Working Group” and other special committees and working groups to discuss the issues of risk management regularly , for accurately control risk issues in different fields.
In the event of a major event or proposal, each responsible unit shall report it to a meeting of operation management or each management committee to decide the necessary measures. Each functional committee not only proactively focus and identify the potential risk issues within internal and external for the company, but bring up appropriate solutions.
The operation record of the RMC is submitted to the chairman for approval. The Internal Audit Office follows up the status of operation and report to the Board of Directors at least once a year to ensure that relevant risk issues are effectively managed.
The company has proactively promoted the mechanism of risk management since 2011.
The followings are the status of main operating over the years.
The Risk Management Committee meeting was convened in April and October 2024 to discuss 17 issues which are submitted by special(functional) committees to discuss the related issues of risk along with the mitigation plans.
.jpg)
The RMC and ESG working group reviews global, local, industrial trends, and identifies relevant risks that are applicable to TWM on a corporate level, discuss the risk prioritization according to the impact levels and the possibility of occurrence.
Annually, an inventory is conducted based on the risk categories and risk items, and each risk
item is further reviewed to adjust the risk description based on emerging international trends. After
evaluating potential impacts, each responsible unit shall select priorities according to risk levels and
adopt corresponding measures and actions to control risks under acceptable range, and risk appetites and
risk tolerances shall be formulated for relevant major risks and submitted to RMC for approval.
Risk Management Policy
Risk tolerance indicators, thresholds of overall gap between target/metric and actual performance that the company is accepting to tolerate, are established and monitored for each risk item. Taking "Changes in customer behavior" and " Sustainable and Responsible Supply Chain Management " as examples:
The risk prioritization, impact of each major risk and mitigating actions, please refer to the Risk Management Matrix and Analysis of Key and Emerging Risks and Opportunities.
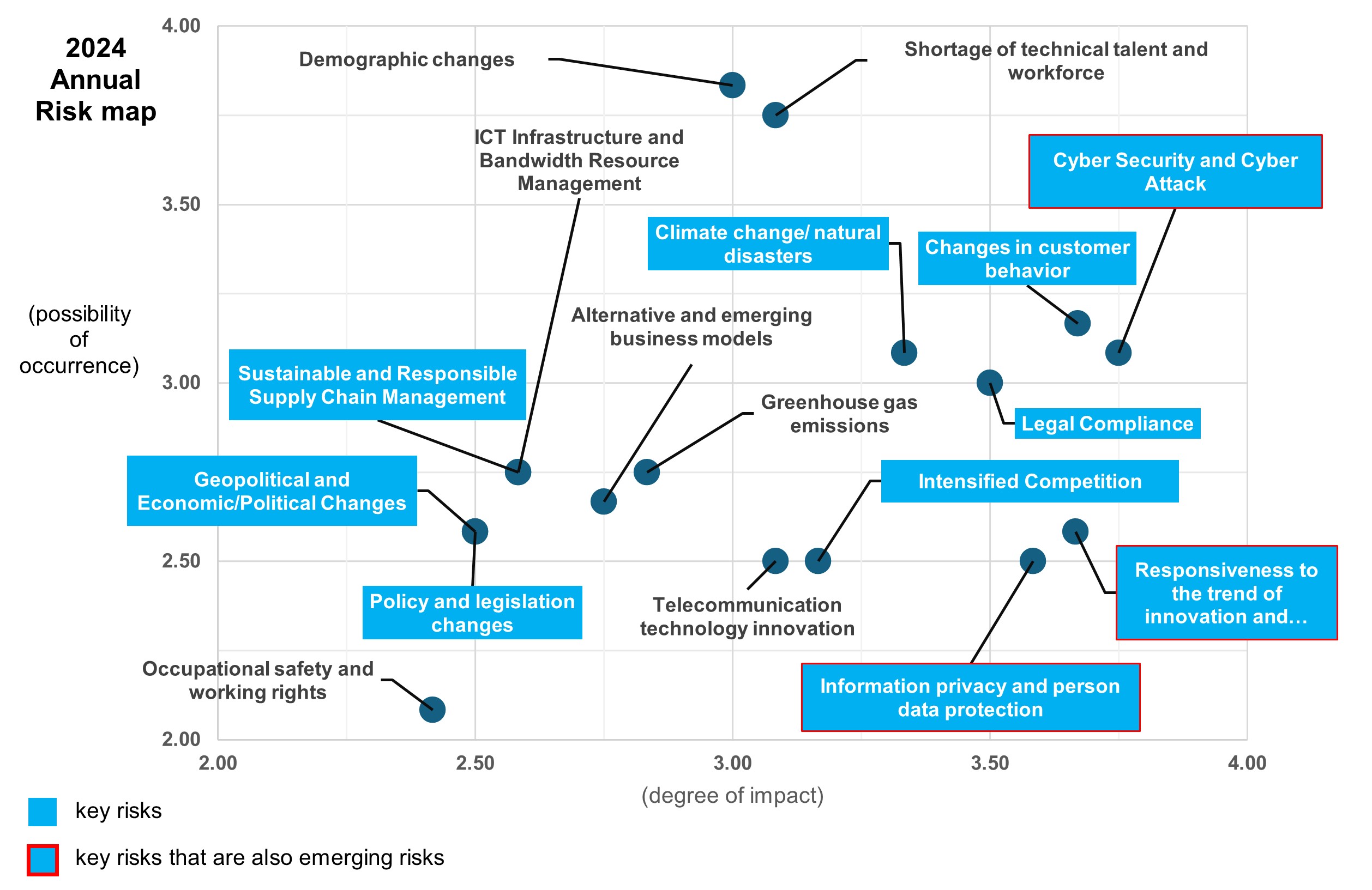
△ Significant Risk
△ Emerging Risk:defined as an emerging and external risk that is
expected to have a significantly long-term impact on the company's business.
| Category | Risk | Emerging Risk correlate with WEF category | TWM Material Topics | Description | Trend | Impact | Mitigating actions | Risk Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory | 1. Legal Compliance △ |
Legitimacy/legal compliance |
|
Remaining stable |
|
|
No penalties have been imposed due to failure regulatory compliance. | |
| 2. Policy and legislation changes △ |
Societal | Legitimacy/legal compliance |
|
Remaining stable |
|
|
Adjacent channel interference | |
| Network bandwidth resources | 3.Climate change/ natural disasters △ |
Environment | Climate change mitigation and adaption |
|
On the decline |
|
|
|
| 4. ICT Infrastructure and Bandwidth Resource Management |
Network quality and coverage |
|
Remaining stable |
|
|
|
||
| 5. Telecommunication technology innovation |
Network quality and coverage |
|
Remaining stable |
|
|
|||
| Information security | 6. Information privacy and person data protection △△ |
Technological | Privacy protection |
|
On the rise |
|
|
Legal Disputes and Customer Complaint Controversies |
| 7. Cyber Security and Cyber Attack △△ |
Technological | Information security |
|
On the rise |
|
|
Information Security Incidents Handling | |
| Business operation | 8. Greenhouse gas emissions |
Climate change mitigation and adaptation |
|
Remaining stable |
|
|
|
|
| 9. Occupational safety and working rights |
Supply chain management | Working rights
|
Remaining Stable | Working rights
|
Working rights
|
Working rights
|
||
| 10. Sustainable and Responsible Supply Chain Management △ |
Supply chain management |
|
Remaining stable |
|
|
|
||
| 11. Infectious disease pandemic and epidemic |
Employee’s physical and mental health |
|
On the decline |
|
|
Symptoms of the same infectious disease occurred within a week on the same floor and in the same unit. | ||
| Market | 12. Product End-of-Life (EOL) management |
Circular economy |
|
|
|
The cumulative recycling target figures are subject to rolling adjustments based on actual annual performance. | ||
| 13. Alternative and emerging business models |
Circular economy |
|
Remaining stable |
|
|
Taiwan Mobile's exclusive plan accounts for over 10% of the total mobile users. | ||
| 14.
Intensified Competition △ |
Risk management |
|
Remaining stable |
|
|
The penetration rate of 5G exceeds 35%. | ||
| 15. Changes in customer behavior △ |
Customer experiences |
|
Remaining stable |
|
|
The "Double Play" plan covers 80% of households nationwide. | ||
| 16. Demographic changes |
Service impact management |
|
Remaining stable |
|
|
Continuously introducing plans tailored for the elderly and vulnerable demographics, with an annual user base surpassing 750K individuals. | ||
| 17. Geopolitical and Economic/Political Changes △ |
Geopolitical | Supply chain management |
|
On the rise | As geopolitical volatility increases, external factors beyond corporate control may intensify.
TWM could face the following operational impacts:
|
|
|
|
| Talent management | 18. Shortage of technical talent and workforce |
Green application and circular economy |
|
On the rise |
|
|
IDP completion rate: below 75% | |
| Innovation management | 19. Responsiveness to the trend of innovation and creativity energy △△ |
Technology innovation & application |
|
On the rise |
|
|
|
Regular risk management education for all non-executive directors
In accordance with Article 40 of《Corporate Governance Best Practice Principles》, the Company requires
directors to complete at least three hours of risk management training annually to enhance their relevant
capabilities. Training programs for directors please reference the company annual report P.41.
Annual report
Focused training throughout the organization on risk management principles
In order to fortify risk response competency of employees and cultivate risk management culture, we
conduct risk management trainings every year with topics such as how to conduct risk management and
information security. We also test employees with simulated phishing
attacks. Such trainings and simulation sessions aim to enhance awareness of employees and train them to
respond effectively in accordance with Company’s regulations. Consequently, creating risk management
culture within the company is a responsibility for all employees, ensuring sustainable business
operations. In 2023, the total number of hours for the risk management course is 78,032.6 hours. In 2024,
the total number of hours for the risk management related courses is 96903.8 hours.
New employee orientation programs include risk management, such as code of conduct, information security training, labor safety and health, and prevention of discrimination and harassment. These programs aim to enable new employees to understand our company culture and our stand on risk.
Financial incentives which incorporate risk management metrics
Employees are encouraged to propose suggestions on how to lower risks and improve the performance and
quality of their work while achieving objectives. Awards will be given to employees in recognition for
suggestions deemed valuable to the company, and these credits will be noted in their evaluation. Employees
with better performance will receive higher bonus and salary increase. On the contrary, if an employee
violates the regulations of internal control system or information security policy, the employee may be
recorded a warning, and may not receive a rewarding performance evaluation. The poor performance ranking
will lead to a lower bonus and salary adjustment.
Incorporation of risk criteria in the development of products and services
As a telecommunications provider of critical infrastructure, Taiwan Mobile fully recognizes that the
stability and security of IT systems are of utmost importance. Accordingly, in the development and
maintenance of our information systems, we not only adhere strictly to security standards but also regard
risk assessment as a core element. From requirements planning to daily operations, every stage
incorporates comprehensive risk assessments to ensure system stability, availability, and information
security, thereby reducing the potential impact of system disruptions or data breaches on our customers
and operations.
In the development of our IT products and services, we primarily conduct risk assessments across three
dimensions: technical architecture and systems, system performance and availability, and information
security and privacy.
We focus on ensuring that the system’s foundational design is robust and sustainable, preventing architectural issues that could hinder future scalability and maintenance.
Key Areas of Assessment:
We ensure that systems can withstand high traffic loads and maintain service stability even under unexpected conditions, thereby delivering a high-quality user experience.
Key Areas of Assessment:
This is the most critical dimension in our development process, aimed at safeguarding both customer and corporate data while ensuring compliance with international security standards.
Key Areas of Assessment:
Through these three dimensions of risk assessment, we ensure that our IT products and services not only meet functional requirements but also deliver a stable, efficient, and secure user experience.